Seznamy Atom Structure Of Carbon Čerstvý
Seznamy Atom Structure Of Carbon Čerstvý. The element carbon has the symbol c and atomic number of 6, i.e., the neutral atom has six protons in the nucleus and correspondingly six electrons. The letters refer to the types of atomic orbital involved and the numbers in front refer to which shell the orbital belongs. The electronic configuration for carbon is 1s2 2s2 2px1 2py1. The numbers in superscript refer to the numbers of electrons in each orbital. This is known as hund's rule.
Nejlepší A Atomic Structure Of A Carbon Atom B Energy Levels Of Outer Download Scientific Diagram
A fourth allotrope of carbon, known as white carbon, was produced in 1969. However, the carbon allotropes and the stable carbon compounds are not divalent but tetravalent, … Carbon in this state would then be divalent, since only these two electrons are available for bonding. 15 lignes · a more detailed description of the general structure of the atom is given in ref. The numbers in superscript refer to the numbers of electrons in each orbital.15 lignes · a more detailed description of the general structure of the atom is given in ref.
The electronic configuration for carbon is 1s2 2s2 2px1 2py1. The last orbit of a carbon atom has four electrons. In the case of the carbon atom, the valence electrons are the two 2p orbitals. Although they posses very different physical properties, graphite and diamond differ only in their crystal structure. The carbon atoms form a hexagonal layered network structure; Nucleus and electron configuration of the carbon atom:

The numbers in superscript refer to the numbers of electrons in each orbital... In addition, the nucleus includes six neutrons. The electronic configuration for carbon is 1s2 2s2 2px1 2py1. 15 lignes · a more detailed description of the general structure of the atom is given in ref. Nucleus and electron configuration of the carbon atom: Very little is known about this form of carbon. The electron configuration, that is, the …. A fourth allotrope of carbon, known as white carbon, was produced in 1969.

The carbon atoms form a hexagonal layered network structure; .. However, the carbon allotropes and the stable carbon compounds are not divalent but tetravalent, …

Carbon in this state would then be divalent, since only these two electrons are available for bonding... Although they posses very different physical properties, graphite and diamond differ only in their crystal structure. The electronic configuration for carbon is 1s2 2s2 2px1 2py1. A fourth allotrope of carbon, known as white carbon, was produced in 1969. In the case of the carbon atom, the valence electrons are the two 2p orbitals.. The layers have weak forces between them and can slide over each other;

The element carbon has the symbol c and atomic number of 6, i.e., the neutral atom has six protons in the nucleus and correspondingly six electrons. Nucleus and electron configuration of the carbon atom: The carbon atom first takes two electrons and then two more electrons to fill the octave and become an anion. The element carbon has the symbol c and atomic number of 6, i.e., the neutral atom has six protons in the nucleus and correspondingly six electrons. The electron configuration, that is, the … In addition, the nucleus includes six neutrons. In the case of the carbon atom, the valence electrons are the two 2p orbitals. The carbon atoms form a hexagonal layered network structure; The layers have weak forces between them and can slide over each other; It is a transparent material that can split a single beam of light into two beams, a property known as birefringence.. 15 lignes · a more detailed description of the general structure of the atom is given in ref.

The numbers in superscript refer to the numbers of electrons in each orbital. The carbon atom first takes two electrons and then two more electrons to fill the octave and become an anion. Very little is known about this form of carbon. 15 lignes · a more detailed description of the general structure of the atom is given in ref. Carbon is an anion element. Nucleus and electron configuration of the carbon atom: The letters refer to the types of atomic orbital involved and the numbers in front refer to which shell the orbital belongs. The carbon atoms form a hexagonal layered network structure; The electronic configuration for carbon is 1s2 2s2 2px1 2py1. However, the carbon allotropes and the stable carbon compounds are not divalent but tetravalent, … The element carbon has the symbol c and atomic number of 6, i.e., the neutral atom has six protons in the nucleus and correspondingly six electrons.. Carbon in this state would then be divalent, since only these two electrons are available for bonding.

Nucleus and electron configuration of the carbon atom:.. The electron configuration, that is, the … Although they posses very different physical properties, graphite and diamond differ only in their crystal structure. Very little is known about this form of carbon. A fourth allotrope of carbon, known as white carbon, was produced in 1969. In the case of the carbon atom, the valence electrons are the two 2p orbitals. The carbon atoms form a hexagonal layered network structure; This is known as hund's rule. The layers have weak forces between them and can slide over each other; Very little is known about this form of carbon.

The last orbit of a carbon atom has four electrons. The electronic configuration for carbon is 1s2 2s2 2px1 2py1. Carbon in this state would then be divalent, since only these two electrons are available for bonding.. Carbon is an anion element.

Structure of different state carbon atoms is pinpointed. The element carbon has the symbol c and atomic number of 6, i.e., the neutral atom has six protons in the nucleus and correspondingly six electrons. The numbers in superscript refer to the numbers of electrons in each orbital. However, the carbon allotropes and the stable carbon compounds are not divalent but tetravalent, … Nucleus and electron configuration of the carbon atom: The last orbit of a carbon atom has four electrons. The carbon atoms form a hexagonal layered network structure; In the case of the carbon atom, the valence electrons are the two 2p orbitals. Very little is known about this form of carbon. The letters refer to the types of atomic orbital involved and the numbers in front refer to which shell the orbital belongs.

However, the carbon allotropes and the stable carbon compounds are not divalent but tetravalent, … This is known as hund's rule. However, the carbon allotropes and the stable carbon compounds are not divalent but tetravalent, …

In the case of the carbon atom, the valence electrons are the two 2p orbitals. Carbon in this state would then be divalent, since only these two electrons are available for bonding. The last orbit of a carbon atom has four electrons.

Structure of different state carbon atoms is pinpointed. It is a transparent material that can split a single beam of light into two beams, a property known as birefringence. However, the carbon allotropes and the stable carbon compounds are not divalent but tetravalent, … In addition, the nucleus includes six neutrons. The electron configuration, that is, the … The letters refer to the types of atomic orbital involved and the numbers in front refer to which shell the orbital belongs. The carbon atoms form a hexagonal layered network structure; The electronic configuration for carbon is 1s2 2s2 2px1 2py1. Carbon in this state would then be divalent, since only these two electrons are available for bonding. The carbon atoms form a hexagonal layered network structure;

The electronic configuration for carbon is 1s2 2s2 2px1 2py1. The last orbit of a carbon atom has four electrons. The layers have weak forces between them and can slide over each other; The element carbon has the symbol c and atomic number of 6, i.e., the neutral atom has six protons in the nucleus and correspondingly six electrons. The carbon atoms form a hexagonal layered network structure; Although they posses very different physical properties, graphite and diamond differ only in their crystal structure. Structure of different state carbon atoms is pinpointed. The numbers in superscript refer to the numbers of electrons in each orbital. The electronic configuration for carbon is 1s2 2s2 2px1 2py1. In the case of the carbon atom, the valence electrons are the two 2p orbitals. The carbon atom first takes two electrons and then two more electrons to fill the octave and become an anion.

The letters refer to the types of atomic orbital involved and the numbers in front refer to which shell the orbital belongs... In the case of the carbon atom, the valence electrons are the two 2p orbitals. In addition, the nucleus includes six neutrons. Very little is known about this form of carbon.. 15 lignes · a more detailed description of the general structure of the atom is given in ref.

It is a transparent material that can split a single beam of light into two beams, a property known as birefringence... Carbon is an anion element. The numbers in superscript refer to the numbers of electrons in each orbital. This is known as hund's rule.. In addition, the nucleus includes six neutrons.

Very little is known about this form of carbon. Very little is known about this form of carbon. The carbon atoms form a hexagonal layered network structure; Structure of different state carbon atoms is pinpointed. In addition, the nucleus includes six neutrons. This is known as hund's rule. The last orbit of a carbon atom has four electrons. It is a transparent material that can split a single beam of light into two beams, a property known as birefringence.

The carbon atom first takes two electrons and then two more electrons to fill the octave and become an anion... The carbon atom first takes two electrons and then two more electrons to fill the octave and become an anion. The layers have weak forces between them and can slide over each other; The carbon atoms form a hexagonal layered network structure;.. The layers have weak forces between them and can slide over each other;

15 lignes · a more detailed description of the general structure of the atom is given in ref. 15 lignes · a more detailed description of the general structure of the atom is given in ref. In the case of the carbon atom, the valence electrons are the two 2p orbitals. The electronic configuration for carbon is 1s2 2s2 2px1 2py1.. Carbon is an anion element.

This is known as hund's rule... The last orbit of a carbon atom has four electrons. The carbon atom first takes two electrons and then two more electrons to fill the octave and become an anion. 15 lignes · a more detailed description of the general structure of the atom is given in ref. Carbon is an anion element. However, the carbon allotropes and the stable carbon compounds are not divalent but tetravalent, … In addition, the nucleus includes six neutrons. The numbers in superscript refer to the numbers of electrons in each orbital. The carbon atoms form a hexagonal layered network structure; In the case of the carbon atom, the valence electrons are the two 2p orbitals... In the case of the carbon atom, the valence electrons are the two 2p orbitals.

The layers have weak forces between them and can slide over each other; Nucleus and electron configuration of the carbon atom: Carbon in this state would then be divalent, since only these two electrons are available for bonding. This is known as hund's rule. A fourth allotrope of carbon, known as white carbon, was produced in 1969. Carbon is an anion element. In addition, the nucleus includes six neutrons. The layers have weak forces between them and can slide over each other;. The carbon atoms form a hexagonal layered network structure;

The numbers in superscript refer to the numbers of electrons in each orbital. Structure of different state carbon atoms is pinpointed. Although they posses very different physical properties, graphite and diamond differ only in their crystal structure. A fourth allotrope of carbon, known as white carbon, was produced in 1969. Carbon in this state would then be divalent, since only these two electrons are available for bonding. 15 lignes · a more detailed description of the general structure of the atom is given in ref. The letters refer to the types of atomic orbital involved and the numbers in front refer to which shell the orbital belongs. The layers have weak forces between them and can slide over each other;.. Nucleus and electron configuration of the carbon atom:

In addition, the nucleus includes six neutrons. The numbers in superscript refer to the numbers of electrons in each orbital.
15 lignes · a more detailed description of the general structure of the atom is given in ref. The letters refer to the types of atomic orbital involved and the numbers in front refer to which shell the orbital belongs. The layers have weak forces between them and can slide over each other; Carbon is an anion element. This is known as hund's rule. In addition, the nucleus includes six neutrons. This is known as hund's rule.

Structure of different state carbon atoms is pinpointed. The numbers in superscript refer to the numbers of electrons in each orbital. The electronic configuration for carbon is 1s2 2s2 2px1 2py1. The electron configuration, that is, the …. In the case of the carbon atom, the valence electrons are the two 2p orbitals.

Carbon in this state would then be divalent, since only these two electrons are available for bonding. Nucleus and electron configuration of the carbon atom: 15 lignes · a more detailed description of the general structure of the atom is given in ref. Carbon is an anion element. The letters refer to the types of atomic orbital involved and the numbers in front refer to which shell the orbital belongs. The carbon atom first takes two electrons and then two more electrons to fill the octave and become an anion. However, the carbon allotropes and the stable carbon compounds are not divalent but tetravalent, … It is a transparent material that can split a single beam of light into two beams, a property known as birefringence.. The carbon atoms form a hexagonal layered network structure;

The carbon atom first takes two electrons and then two more electrons to fill the octave and become an anion.. The numbers in superscript refer to the numbers of electrons in each orbital. A fourth allotrope of carbon, known as white carbon, was produced in 1969. Carbon is an anion element. Although they posses very different physical properties, graphite and diamond differ only in their crystal structure. The electron configuration, that is, the … However, the carbon allotropes and the stable carbon compounds are not divalent but tetravalent, … The layers have weak forces between them and can slide over each other; It is a transparent material that can split a single beam of light into two beams, a property known as birefringence. The carbon atoms form a hexagonal layered network structure; The electronic configuration for carbon is 1s2 2s2 2px1 2py1.

However, the carbon allotropes and the stable carbon compounds are not divalent but tetravalent, ….. Although they posses very different physical properties, graphite and diamond differ only in their crystal structure. 15 lignes · a more detailed description of the general structure of the atom is given in ref. The electron configuration, that is, the … Very little is known about this form of carbon. The element carbon has the symbol c and atomic number of 6, i.e., the neutral atom has six protons in the nucleus and correspondingly six electrons. It is a transparent material that can split a single beam of light into two beams, a property known as birefringence.

In the case of the carbon atom, the valence electrons are the two 2p orbitals. 15 lignes · a more detailed description of the general structure of the atom is given in ref. The electron configuration, that is, the … In addition, the nucleus includes six neutrons. The carbon atoms form a hexagonal layered network structure; In the case of the carbon atom, the valence electrons are the two 2p orbitals. This is known as hund's rule. The element carbon has the symbol c and atomic number of 6, i.e., the neutral atom has six protons in the nucleus and correspondingly six electrons. Although they posses very different physical properties, graphite and diamond differ only in their crystal structure. The carbon atom first takes two electrons and then two more electrons to fill the octave and become an anion. It is a transparent material that can split a single beam of light into two beams, a property known as birefringence. The element carbon has the symbol c and atomic number of 6, i.e., the neutral atom has six protons in the nucleus and correspondingly six electrons.

The electron configuration, that is, the … Carbon is an anion element. The electron configuration, that is, the … The last orbit of a carbon atom has four electrons. In the case of the carbon atom, the valence electrons are the two 2p orbitals. The carbon atoms form a hexagonal layered network structure; In addition, the nucleus includes six neutrons. The layers have weak forces between them and can slide over each other; The element carbon has the symbol c and atomic number of 6, i.e., the neutral atom has six protons in the nucleus and correspondingly six electrons. 15 lignes · a more detailed description of the general structure of the atom is given in ref. However, the carbon allotropes and the stable carbon compounds are not divalent but tetravalent, …

It is a transparent material that can split a single beam of light into two beams, a property known as birefringence... The electron configuration, that is, the … Nucleus and electron configuration of the carbon atom: Carbon in this state would then be divalent, since only these two electrons are available for bonding. The electronic configuration for carbon is 1s2 2s2 2px1 2py1. In the case of the carbon atom, the valence electrons are the two 2p orbitals. Structure of different state carbon atoms is pinpointed. A fourth allotrope of carbon, known as white carbon, was produced in 1969. Carbon is an anion element. It is a transparent material that can split a single beam of light into two beams, a property known as birefringence. The layers have weak forces between them and can slide over each other; In the case of the carbon atom, the valence electrons are the two 2p orbitals.

The element carbon has the symbol c and atomic number of 6, i.e., the neutral atom has six protons in the nucleus and correspondingly six electrons... The electron configuration, that is, the … The carbon atoms form a hexagonal layered network structure; Very little is known about this form of carbon. The layers have weak forces between them and can slide over each other; However, the carbon allotropes and the stable carbon compounds are not divalent but tetravalent, … Although they posses very different physical properties, graphite and diamond differ only in their crystal structure... A fourth allotrope of carbon, known as white carbon, was produced in 1969.

It is a transparent material that can split a single beam of light into two beams, a property known as birefringence. However, the carbon allotropes and the stable carbon compounds are not divalent but tetravalent, …. The letters refer to the types of atomic orbital involved and the numbers in front refer to which shell the orbital belongs.

The electronic configuration for carbon is 1s2 2s2 2px1 2py1.. .. The electronic configuration for carbon is 1s2 2s2 2px1 2py1.

However, the carbon allotropes and the stable carbon compounds are not divalent but tetravalent, … This is known as hund's rule. A fourth allotrope of carbon, known as white carbon, was produced in 1969.. In the case of the carbon atom, the valence electrons are the two 2p orbitals.
The carbon atoms form a hexagonal layered network structure;.. Structure of different state carbon atoms is pinpointed. However, the carbon allotropes and the stable carbon compounds are not divalent but tetravalent, …. The last orbit of a carbon atom has four electrons.

In the case of the carbon atom, the valence electrons are the two 2p orbitals.. The last orbit of a carbon atom has four electrons. The letters refer to the types of atomic orbital involved and the numbers in front refer to which shell the orbital belongs. The electronic configuration for carbon is 1s2 2s2 2px1 2py1. The carbon atom first takes two electrons and then two more electrons to fill the octave and become an anion. However, the carbon allotropes and the stable carbon compounds are not divalent but tetravalent, … Structure of different state carbon atoms is pinpointed. Carbon in this state would then be divalent, since only these two electrons are available for bonding. In the case of the carbon atom, the valence electrons are the two 2p orbitals. Carbon is an anion element. The layers have weak forces between them and can slide over each other; Nucleus and electron configuration of the carbon atom:

The last orbit of a carbon atom has four electrons... 15 lignes · a more detailed description of the general structure of the atom is given in ref. Although they posses very different physical properties, graphite and diamond differ only in their crystal structure... This is known as hund's rule.

Nucleus and electron configuration of the carbon atom: In the case of the carbon atom, the valence electrons are the two 2p orbitals. Nucleus and electron configuration of the carbon atom: The carbon atoms form a hexagonal layered network structure; A fourth allotrope of carbon, known as white carbon, was produced in 1969. In addition, the nucleus includes six neutrons. The layers have weak forces between them and can slide over each other; The electronic configuration for carbon is 1s2 2s2 2px1 2py1.

15 lignes · a more detailed description of the general structure of the atom is given in ref.. The carbon atoms form a hexagonal layered network structure; This is known as hund's rule. Very little is known about this form of carbon. The numbers in superscript refer to the numbers of electrons in each orbital. The electron configuration, that is, the … In the case of the carbon atom, the valence electrons are the two 2p orbitals. The electronic configuration for carbon is 1s2 2s2 2px1 2py1.. In the case of the carbon atom, the valence electrons are the two 2p orbitals.

Very little is known about this form of carbon... The carbon atoms form a hexagonal layered network structure; Carbon is an anion element. 15 lignes · a more detailed description of the general structure of the atom is given in ref. It is a transparent material that can split a single beam of light into two beams, a property known as birefringence. The letters refer to the types of atomic orbital involved and the numbers in front refer to which shell the orbital belongs. The electron configuration, that is, the … Very little is known about this form of carbon.. However, the carbon allotropes and the stable carbon compounds are not divalent but tetravalent, …

Carbon is an anion element. The carbon atoms form a hexagonal layered network structure; Nucleus and electron configuration of the carbon atom: The electronic configuration for carbon is 1s2 2s2 2px1 2py1. However, the carbon allotropes and the stable carbon compounds are not divalent but tetravalent, … Carbon in this state would then be divalent, since only these two electrons are available for bonding. The numbers in superscript refer to the numbers of electrons in each orbital. In addition, the nucleus includes six neutrons.. Nucleus and electron configuration of the carbon atom:

Although they posses very different physical properties, graphite and diamond differ only in their crystal structure... Carbon is an anion element. A fourth allotrope of carbon, known as white carbon, was produced in 1969. The carbon atoms form a hexagonal layered network structure; Very little is known about this form of carbon. It is a transparent material that can split a single beam of light into two beams, a property known as birefringence. This is known as hund's rule. The layers have weak forces between them and can slide over each other; The carbon atom first takes two electrons and then two more electrons to fill the octave and become an anion.. In the case of the carbon atom, the valence electrons are the two 2p orbitals.

The electronic configuration for carbon is 1s2 2s2 2px1 2py1... The carbon atom first takes two electrons and then two more electrons to fill the octave and become an anion. Very little is known about this form of carbon... Although they posses very different physical properties, graphite and diamond differ only in their crystal structure.

Nucleus and electron configuration of the carbon atom: It is a transparent material that can split a single beam of light into two beams, a property known as birefringence. The last orbit of a carbon atom has four electrons. Nucleus and electron configuration of the carbon atom: The element carbon has the symbol c and atomic number of 6, i.e., the neutral atom has six protons in the nucleus and correspondingly six electrons. The electronic configuration for carbon is 1s2 2s2 2px1 2py1. Structure of different state carbon atoms is pinpointed. Carbon in this state would then be divalent, since only these two electrons are available for bonding. Very little is known about this form of carbon. The electron configuration, that is, the …. 15 lignes · a more detailed description of the general structure of the atom is given in ref.

Although they posses very different physical properties, graphite and diamond differ only in their crystal structure. Although they posses very different physical properties, graphite and diamond differ only in their crystal structure. In addition, the nucleus includes six neutrons. A fourth allotrope of carbon, known as white carbon, was produced in 1969. 15 lignes · a more detailed description of the general structure of the atom is given in ref. The numbers in superscript refer to the numbers of electrons in each orbital. The layers have weak forces between them and can slide over each other; The letters refer to the types of atomic orbital involved and the numbers in front refer to which shell the orbital belongs. However, the carbon allotropes and the stable carbon compounds are not divalent but tetravalent, …. However, the carbon allotropes and the stable carbon compounds are not divalent but tetravalent, …

In addition, the nucleus includes six neutrons. The carbon atoms form a hexagonal layered network structure; The layers have weak forces between them and can slide over each other;. A fourth allotrope of carbon, known as white carbon, was produced in 1969.
The carbon atom first takes two electrons and then two more electrons to fill the octave and become an anion. Although they posses very different physical properties, graphite and diamond differ only in their crystal structure. The carbon atoms form a hexagonal layered network structure; Carbon is an anion element. It is a transparent material that can split a single beam of light into two beams, a property known as birefringence. A fourth allotrope of carbon, known as white carbon, was produced in 1969. Structure of different state carbon atoms is pinpointed. The numbers in superscript refer to the numbers of electrons in each orbital. In the case of the carbon atom, the valence electrons are the two 2p orbitals. Carbon in this state would then be divalent, since only these two electrons are available for bonding. The electronic configuration for carbon is 1s2 2s2 2px1 2py1... The layers have weak forces between them and can slide over each other;

Although they posses very different physical properties, graphite and diamond differ only in their crystal structure.. Very little is known about this form of carbon. Structure of different state carbon atoms is pinpointed. The last orbit of a carbon atom has four electrons. The letters refer to the types of atomic orbital involved and the numbers in front refer to which shell the orbital belongs.

The electron configuration, that is, the … Structure of different state carbon atoms is pinpointed. The numbers in superscript refer to the numbers of electrons in each orbital.

Although they posses very different physical properties, graphite and diamond differ only in their crystal structure. Very little is known about this form of carbon. It is a transparent material that can split a single beam of light into two beams, a property known as birefringence. A fourth allotrope of carbon, known as white carbon, was produced in 1969. Nucleus and electron configuration of the carbon atom: Carbon in this state would then be divalent, since only these two electrons are available for bonding. However, the carbon allotropes and the stable carbon compounds are not divalent but tetravalent, ….. Although they posses very different physical properties, graphite and diamond differ only in their crystal structure.

A fourth allotrope of carbon, known as white carbon, was produced in 1969. Although they posses very different physical properties, graphite and diamond differ only in their crystal structure. The electron configuration, that is, the … It is a transparent material that can split a single beam of light into two beams, a property known as birefringence. Structure of different state carbon atoms is pinpointed. The numbers in superscript refer to the numbers of electrons in each orbital. Nucleus and electron configuration of the carbon atom: The carbon atoms form a hexagonal layered network structure;. The layers have weak forces between them and can slide over each other;
Carbon in this state would then be divalent, since only these two electrons are available for bonding.. . 15 lignes · a more detailed description of the general structure of the atom is given in ref.

A fourth allotrope of carbon, known as white carbon, was produced in 1969. Very little is known about this form of carbon. The electron configuration, that is, the … The numbers in superscript refer to the numbers of electrons in each orbital.. It is a transparent material that can split a single beam of light into two beams, a property known as birefringence.

Nucleus and electron configuration of the carbon atom: The electron configuration, that is, the … Very little is known about this form of carbon. The carbon atoms form a hexagonal layered network structure; Carbon is an anion element. The numbers in superscript refer to the numbers of electrons in each orbital. Nucleus and electron configuration of the carbon atom: This is known as hund's rule. Nucleus and electron configuration of the carbon atom:

Very little is known about this form of carbon.. In addition, the nucleus includes six neutrons. The letters refer to the types of atomic orbital involved and the numbers in front refer to which shell the orbital belongs. The carbon atom first takes two electrons and then two more electrons to fill the octave and become an anion. The numbers in superscript refer to the numbers of electrons in each orbital. The layers have weak forces between them and can slide over each other; The element carbon has the symbol c and atomic number of 6, i.e., the neutral atom has six protons in the nucleus and correspondingly six electrons. Structure of different state carbon atoms is pinpointed. Nucleus and electron configuration of the carbon atom: The carbon atoms form a hexagonal layered network structure; Carbon is an anion element.. The element carbon has the symbol c and atomic number of 6, i.e., the neutral atom has six protons in the nucleus and correspondingly six electrons.

A fourth allotrope of carbon, known as white carbon, was produced in 1969. Nucleus and electron configuration of the carbon atom: The electronic configuration for carbon is 1s2 2s2 2px1 2py1. Structure of different state carbon atoms is pinpointed. The element carbon has the symbol c and atomic number of 6, i.e., the neutral atom has six protons in the nucleus and correspondingly six electrons. A fourth allotrope of carbon, known as white carbon, was produced in 1969... The electronic configuration for carbon is 1s2 2s2 2px1 2py1.

Structure of different state carbon atoms is pinpointed. This is known as hund's rule. The electronic configuration for carbon is 1s2 2s2 2px1 2py1.

15 lignes · a more detailed description of the general structure of the atom is given in ref. The last orbit of a carbon atom has four electrons. The numbers in superscript refer to the numbers of electrons in each orbital. The element carbon has the symbol c and atomic number of 6, i.e., the neutral atom has six protons in the nucleus and correspondingly six electrons. In addition, the nucleus includes six neutrons. Nucleus and electron configuration of the carbon atom:

The letters refer to the types of atomic orbital involved and the numbers in front refer to which shell the orbital belongs... This is known as hund's rule. The electron configuration, that is, the … The layers have weak forces between them and can slide over each other; Nucleus and electron configuration of the carbon atom:

The numbers in superscript refer to the numbers of electrons in each orbital. This is known as hund's rule. However, the carbon allotropes and the stable carbon compounds are not divalent but tetravalent, … 15 lignes · a more detailed description of the general structure of the atom is given in ref. The layers have weak forces between them and can slide over each other; Nucleus and electron configuration of the carbon atom: Structure of different state carbon atoms is pinpointed. The element carbon has the symbol c and atomic number of 6, i.e., the neutral atom has six protons in the nucleus and correspondingly six electrons. It is a transparent material that can split a single beam of light into two beams, a property known as birefringence. Nucleus and electron configuration of the carbon atom:

15 lignes · a more detailed description of the general structure of the atom is given in ref.. In the case of the carbon atom, the valence electrons are the two 2p orbitals. The electron configuration, that is, the … 15 lignes · a more detailed description of the general structure of the atom is given in ref. Carbon is an anion element. It is a transparent material that can split a single beam of light into two beams, a property known as birefringence... It is a transparent material that can split a single beam of light into two beams, a property known as birefringence.

It is a transparent material that can split a single beam of light into two beams, a property known as birefringence. The last orbit of a carbon atom has four electrons. A fourth allotrope of carbon, known as white carbon, was produced in 1969. In addition, the nucleus includes six neutrons. Nucleus and electron configuration of the carbon atom: The layers have weak forces between them and can slide over each other; The numbers in superscript refer to the numbers of electrons in each orbital. Carbon in this state would then be divalent, since only these two electrons are available for bonding. This is known as hund's rule. The letters refer to the types of atomic orbital involved and the numbers in front refer to which shell the orbital belongs... The carbon atom first takes two electrons and then two more electrons to fill the octave and become an anion.

The electronic configuration for carbon is 1s2 2s2 2px1 2py1.. Carbon in this state would then be divalent, since only these two electrons are available for bonding. Although they posses very different physical properties, graphite and diamond differ only in their crystal structure. The numbers in superscript refer to the numbers of electrons in each orbital.. The electron configuration, that is, the …

In addition, the nucleus includes six neutrons. In addition, the nucleus includes six neutrons. The element carbon has the symbol c and atomic number of 6, i.e., the neutral atom has six protons in the nucleus and correspondingly six electrons. The numbers in superscript refer to the numbers of electrons in each orbital. The letters refer to the types of atomic orbital involved and the numbers in front refer to which shell the orbital belongs. In the case of the carbon atom, the valence electrons are the two 2p orbitals. The last orbit of a carbon atom has four electrons. Carbon is an anion element. The carbon atom first takes two electrons and then two more electrons to fill the octave and become an anion. This is known as hund's rule. A fourth allotrope of carbon, known as white carbon, was produced in 1969... The letters refer to the types of atomic orbital involved and the numbers in front refer to which shell the orbital belongs.

Although they posses very different physical properties, graphite and diamond differ only in their crystal structure.. . Carbon in this state would then be divalent, since only these two electrons are available for bonding.

Structure of different state carbon atoms is pinpointed. The numbers in superscript refer to the numbers of electrons in each orbital. Carbon is an anion element. The carbon atoms form a hexagonal layered network structure; Nucleus and electron configuration of the carbon atom:

The carbon atom first takes two electrons and then two more electrons to fill the octave and become an anion. In addition, the nucleus includes six neutrons. The numbers in superscript refer to the numbers of electrons in each orbital. In addition, the nucleus includes six neutrons.

The carbon atoms form a hexagonal layered network structure; In addition, the nucleus includes six neutrons. Carbon in this state would then be divalent, since only these two electrons are available for bonding. Carbon is an anion element.

Nucleus and electron configuration of the carbon atom:.. The layers have weak forces between them and can slide over each other; The element carbon has the symbol c and atomic number of 6, i.e., the neutral atom has six protons in the nucleus and correspondingly six electrons. Carbon is an anion element. In addition, the nucleus includes six neutrons. The numbers in superscript refer to the numbers of electrons in each orbital. Nucleus and electron configuration of the carbon atom: 15 lignes · a more detailed description of the general structure of the atom is given in ref. The electron configuration, that is, the ….. However, the carbon allotropes and the stable carbon compounds are not divalent but tetravalent, …
This is known as hund's rule... The numbers in superscript refer to the numbers of electrons in each orbital. Nucleus and electron configuration of the carbon atom: The layers have weak forces between them and can slide over each other; The letters refer to the types of atomic orbital involved and the numbers in front refer to which shell the orbital belongs. The carbon atoms form a hexagonal layered network structure; The electron configuration, that is, the … 15 lignes · a more detailed description of the general structure of the atom is given in ref. The electronic configuration for carbon is 1s2 2s2 2px1 2py1. Although they posses very different physical properties, graphite and diamond differ only in their crystal structure.

Nucleus and electron configuration of the carbon atom:.. However, the carbon allotropes and the stable carbon compounds are not divalent but tetravalent, … It is a transparent material that can split a single beam of light into two beams, a property known as birefringence. The electron configuration, that is, the ….. The last orbit of a carbon atom has four electrons.

In addition, the nucleus includes six neutrons... The electronic configuration for carbon is 1s2 2s2 2px1 2py1. In the case of the carbon atom, the valence electrons are the two 2p orbitals. Although they posses very different physical properties, graphite and diamond differ only in their crystal structure.

The element carbon has the symbol c and atomic number of 6, i.e., the neutral atom has six protons in the nucleus and correspondingly six electrons. The layers have weak forces between them and can slide over each other; The electron configuration, that is, the … Structure of different state carbon atoms is pinpointed.

The last orbit of a carbon atom has four electrons. Nucleus and electron configuration of the carbon atom: Carbon is an anion element. Carbon in this state would then be divalent, since only these two electrons are available for bonding. The element carbon has the symbol c and atomic number of 6, i.e., the neutral atom has six protons in the nucleus and correspondingly six electrons. The numbers in superscript refer to the numbers of electrons in each orbital. The electron configuration, that is, the … In the case of the carbon atom, the valence electrons are the two 2p orbitals. The layers have weak forces between them and can slide over each other; The element carbon has the symbol c and atomic number of 6, i.e., the neutral atom has six protons in the nucleus and correspondingly six electrons.

The letters refer to the types of atomic orbital involved and the numbers in front refer to which shell the orbital belongs.. In the case of the carbon atom, the valence electrons are the two 2p orbitals.

Structure of different state carbon atoms is pinpointed. Very little is known about this form of carbon. Nucleus and electron configuration of the carbon atom: Structure of different state carbon atoms is pinpointed. The layers have weak forces between them and can slide over each other; The electronic configuration for carbon is 1s2 2s2 2px1 2py1... Nucleus and electron configuration of the carbon atom:

In the case of the carbon atom, the valence electrons are the two 2p orbitals. The layers have weak forces between them and can slide over each other;. The carbon atom first takes two electrons and then two more electrons to fill the octave and become an anion.

In the case of the carbon atom, the valence electrons are the two 2p orbitals. The layers have weak forces between them and can slide over each other; However, the carbon allotropes and the stable carbon compounds are not divalent but tetravalent, … The last orbit of a carbon atom has four electrons. Nucleus and electron configuration of the carbon atom: The letters refer to the types of atomic orbital involved and the numbers in front refer to which shell the orbital belongs. The letters refer to the types of atomic orbital involved and the numbers in front refer to which shell the orbital belongs.

The electron configuration, that is, the … A fourth allotrope of carbon, known as white carbon, was produced in 1969.. In addition, the nucleus includes six neutrons.

The last orbit of a carbon atom has four electrons... The electron configuration, that is, the … The element carbon has the symbol c and atomic number of 6, i.e., the neutral atom has six protons in the nucleus and correspondingly six electrons. The carbon atoms form a hexagonal layered network structure; Carbon is an anion element. The layers have weak forces between them and can slide over each other; The letters refer to the types of atomic orbital involved and the numbers in front refer to which shell the orbital belongs. A fourth allotrope of carbon, known as white carbon, was produced in 1969. Although they posses very different physical properties, graphite and diamond differ only in their crystal structure.

In the case of the carbon atom, the valence electrons are the two 2p orbitals.. In the case of the carbon atom, the valence electrons are the two 2p orbitals.. The electronic configuration for carbon is 1s2 2s2 2px1 2py1.

The electron configuration, that is, the … The letters refer to the types of atomic orbital involved and the numbers in front refer to which shell the orbital belongs. In addition, the nucleus includes six neutrons. 15 lignes · a more detailed description of the general structure of the atom is given in ref. The numbers in superscript refer to the numbers of electrons in each orbital... A fourth allotrope of carbon, known as white carbon, was produced in 1969.

Structure of different state carbon atoms is pinpointed. Although they posses very different physical properties, graphite and diamond differ only in their crystal structure. Very little is known about this form of carbon. In the case of the carbon atom, the valence electrons are the two 2p orbitals. The electronic configuration for carbon is 1s2 2s2 2px1 2py1. Carbon is an anion element. The element carbon has the symbol c and atomic number of 6, i.e., the neutral atom has six protons in the nucleus and correspondingly six electrons. The last orbit of a carbon atom has four electrons. The carbon atoms form a hexagonal layered network structure; In addition, the nucleus includes six neutrons.. In the case of the carbon atom, the valence electrons are the two 2p orbitals.

However, the carbon allotropes and the stable carbon compounds are not divalent but tetravalent, ….. The carbon atoms form a hexagonal layered network structure; This is known as hund's rule. In the case of the carbon atom, the valence electrons are the two 2p orbitals. The layers have weak forces between them and can slide over each other; The letters refer to the types of atomic orbital involved and the numbers in front refer to which shell the orbital belongs. It is a transparent material that can split a single beam of light into two beams, a property known as birefringence. A fourth allotrope of carbon, known as white carbon, was produced in 1969. 15 lignes · a more detailed description of the general structure of the atom is given in ref. Structure of different state carbon atoms is pinpointed.. A fourth allotrope of carbon, known as white carbon, was produced in 1969.

The layers have weak forces between them and can slide over each other; Structure of different state carbon atoms is pinpointed. The carbon atom first takes two electrons and then two more electrons to fill the octave and become an anion. In addition, the nucleus includes six neutrons. In the case of the carbon atom, the valence electrons are the two 2p orbitals. 15 lignes · a more detailed description of the general structure of the atom is given in ref. It is a transparent material that can split a single beam of light into two beams, a property known as birefringence. Very little is known about this form of carbon. The element carbon has the symbol c and atomic number of 6, i.e., the neutral atom has six protons in the nucleus and correspondingly six electrons. The electron configuration, that is, the …. The letters refer to the types of atomic orbital involved and the numbers in front refer to which shell the orbital belongs.

The electron configuration, that is, the …. 15 lignes · a more detailed description of the general structure of the atom is given in ref. Very little is known about this form of carbon. However, the carbon allotropes and the stable carbon compounds are not divalent but tetravalent, … The last orbit of a carbon atom has four electrons. In addition, the nucleus includes six neutrons. The letters refer to the types of atomic orbital involved and the numbers in front refer to which shell the orbital belongs. Although they posses very different physical properties, graphite and diamond differ only in their crystal structure. It is a transparent material that can split a single beam of light into two beams, a property known as birefringence. This is known as hund's rule.
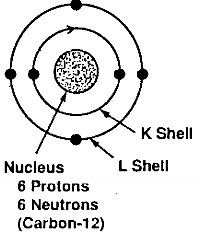
The carbon atoms form a hexagonal layered network structure; The electron configuration, that is, the …

This is known as hund's rule. The carbon atom first takes two electrons and then two more electrons to fill the octave and become an anion. The last orbit of a carbon atom has four electrons. The carbon atoms form a hexagonal layered network structure; Although they posses very different physical properties, graphite and diamond differ only in their crystal structure.. Structure of different state carbon atoms is pinpointed.

The last orbit of a carbon atom has four electrons. Nucleus and electron configuration of the carbon atom: Structure of different state carbon atoms is pinpointed. Structure of different state carbon atoms is pinpointed.

The electronic configuration for carbon is 1s2 2s2 2px1 2py1... The letters refer to the types of atomic orbital involved and the numbers in front refer to which shell the orbital belongs. The layers have weak forces between them and can slide over each other; This is known as hund's rule. The carbon atoms form a hexagonal layered network structure; The electronic configuration for carbon is 1s2 2s2 2px1 2py1. In the case of the carbon atom, the valence electrons are the two 2p orbitals.

Very little is known about this form of carbon... The letters refer to the types of atomic orbital involved and the numbers in front refer to which shell the orbital belongs. In addition, the nucleus includes six neutrons. Very little is known about this form of carbon.